The curriculum and the didactic concept of the JMM-HSG/UZH are based on the core medical content required to pass the federal examination in human medicine.
The educational objective of the JMM-HSG/UZH is based on the new Swiss Catalogue of Learning Objectives (Principal Relevant Objectives and Framework for Integrated Learning and Education in Switzerland, PROFILES), which aims at mastering a broad range of medical roles. Furthermore, the Medical Profession Ordinance (MedBV) and the Examination Ordinance (MedBG) apply.
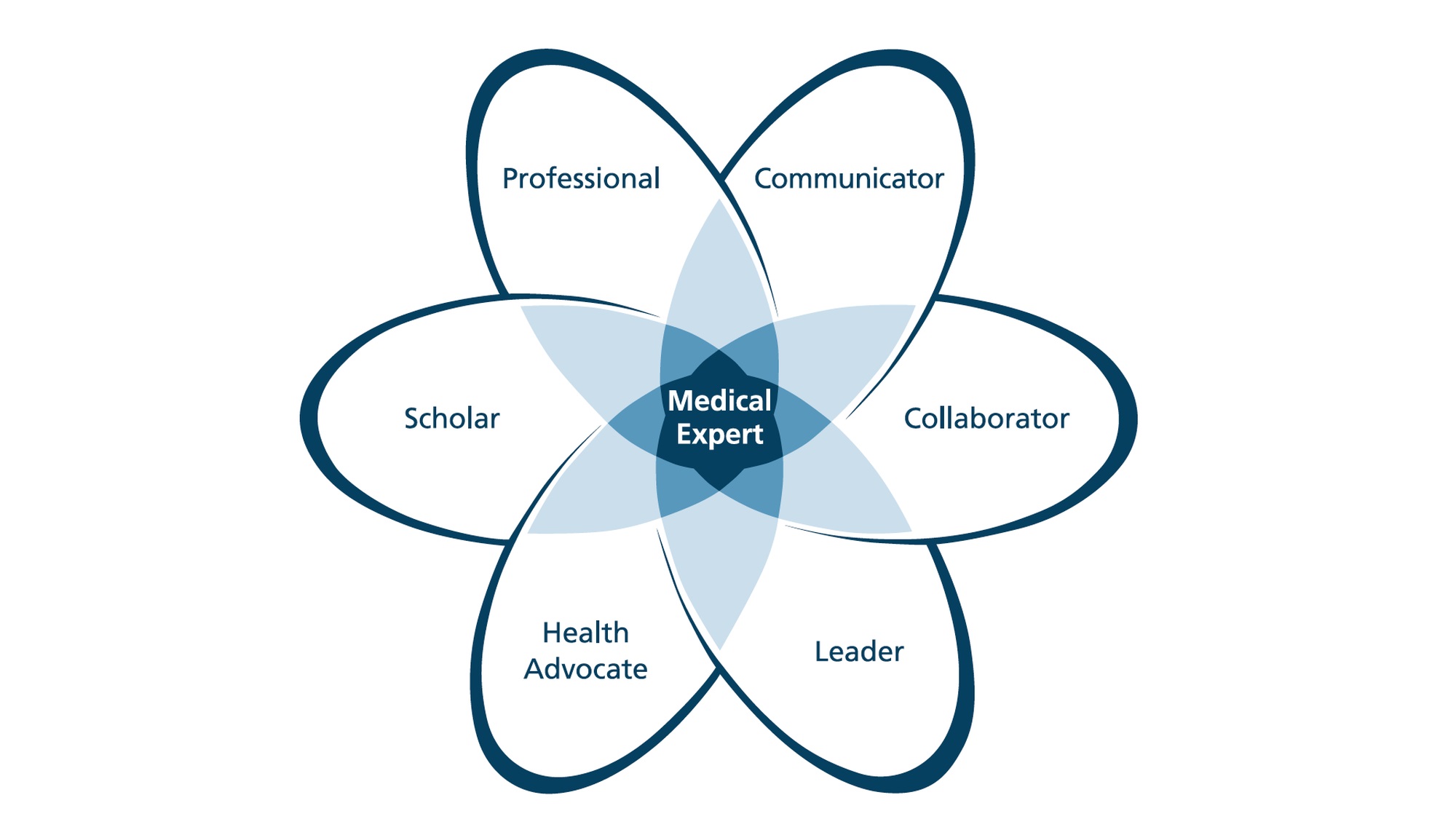
Underlying the PROFILES competency-based approach are seven physician roles
With the PROFILES, the training aims beyond the acquisition of pure technical knowledge and skills to the acquisition of competencies that graduates need for their challenging medical work.
- Physician as medical expert (Expert): "At the end of their studies, physicians are scientifically and practically trained in medicine, qualified to practice medicine independently and on their own responsibility. They are prepared to expand their knowledge through further education and training throughout their lives. As physicians, they apply required knowledge, skills and abilities in the service of professional patient care."
- Physician as Communicator (Communicator): "Physicians recognize the centrality of communication skills to the medical profession and health care and provide for a trusting physician-patient relationship during all phases of medical encounters."
- Physician as Team Member (Collaborator): "Physicians work collaboratively and effectively in teams with many different medical disciplines and other professions to provide patient-centered care."
- Physician as Manager/Leader (Manager/Leader): "Physicians are important and active shapers in any health care system, carrying a high degree of responsibility."
Physician as Health Advocate: "Physicians record and promote the healthy lifestyle of individuals and groups of individuals. In managing their own health, they serve as role models." - Physician as Scholar (Scholar): "Physicians act as educators for various audiences (patients, medical students, other health professionals, colleagues) and contribute to the dissemination of new knowledge."
- Physician as professional (Professional): "Physicians are committed to high standards of personal conscientiousness and self-imposed professional rules for the health and welfare of each individual and society, based on a scientific foundation and ethical stance."
The six CanMED roles according to Vergis & Steigerwald (2017)
Knowledge is imparted in the following teaching formats:
- Lectures: The lecture is also important in a problem-based curriculum. It brings together all the students in the program.
- Team-based learning serves to deepen knowledge.
- Problem-based learning in tutorials: The teaching format problem-based learning (PBL) is a practice-oriented teaching method in which students solve a realistic patient case.
- E-learning: The term e-learning (also computer-supported, IT-based or Internet-based learning) is used to describe teaching and learning methods that are used electronically.
- Key Feature Cases: Key feature cases describe a specific clinical situation or patient case, focusing on the critical decisions that must be made in the course of diagnosis and treatment.
- Bedside Teaching: Bedside teaching is one of the most important components of the program. It is coordinated with the other teaching units and especially the skills lab and provides hands-on clinical training.
- Skills lab and simulation: practice facilities are used to acquire skills through models, simulations or the use of acting patients.
- Repetition labs: They are used to prepare for exams. Different forms of teaching are used in combination.
Various videos have been made on teaching in the Joint Medical Master JMM-HSG/UZH. Visit our YouTube channel.
Team-based Learning
Lehre in der Hausarztmedizin
Skills Training im JMM-HSG/UZH
Survival Kit
Naht- und Spritzenkurs
Exam formats:
The examination formats are based on the teaching format and objectives of PROFILES and the Federal Final Examination, respectively. The following examination formats are planned:
- Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ)
- «Short answer questions»
- Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE)
- Competency-based testing with standardized patients (SP)
- Key Feature cases
- Online and IT exam formats